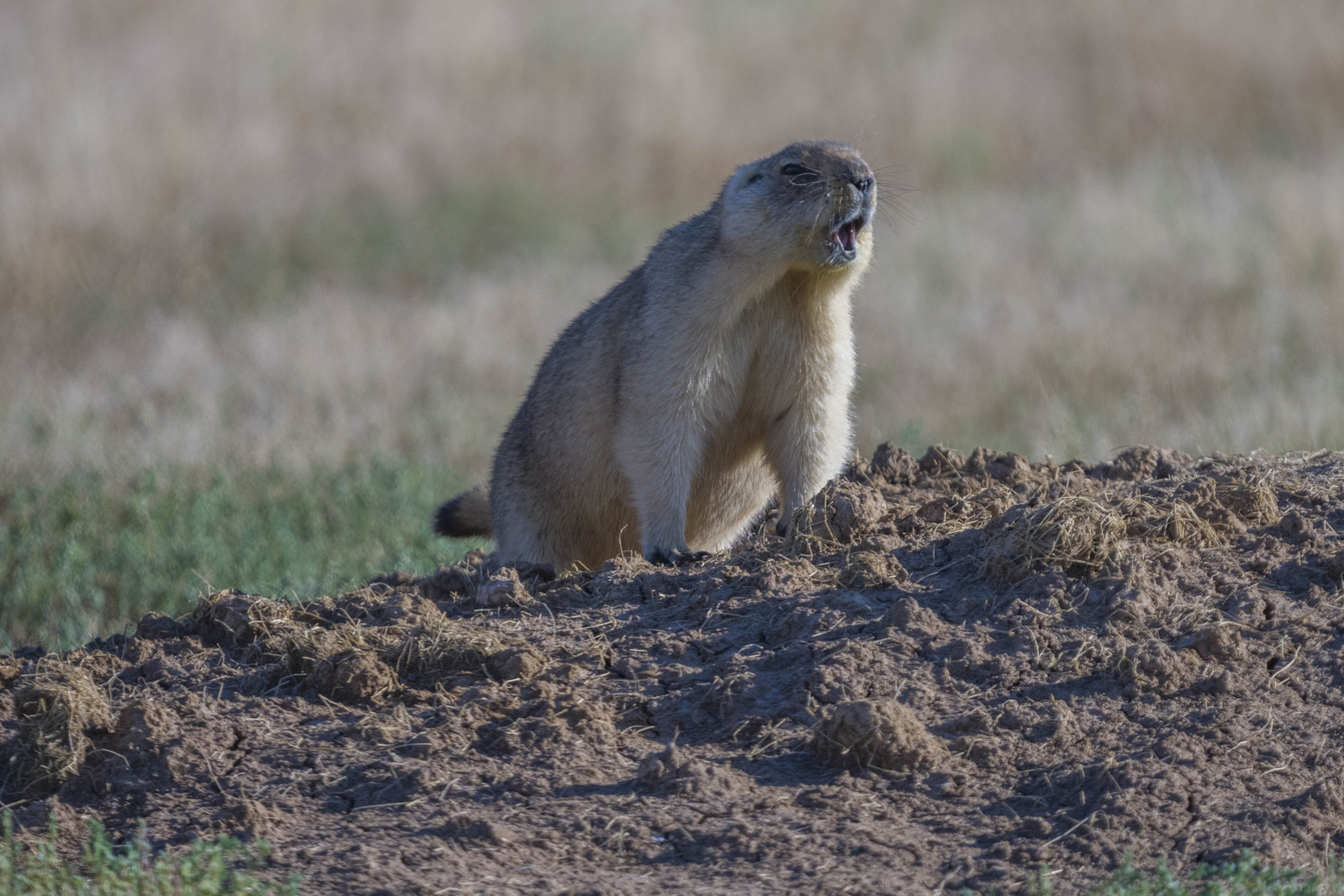
Population: As aresult of intensive plowing of virgin and fallow lands in the northern andcentral regions of Kazakhstan in 1953-1954, the number decreased. It has beenpreserved mainly in sparsely populated and untilled steppes.Status.Non-endangered and non-game species but with ecological and cultural significance.Habitat.In Kazakhstan, the steppe marmot is found in the Kostanay region (Fedorovsky, Mendykarinsky and Presnogorkovsky districts), in the Presnovskydistrict of the North Kazakhstan region. The northern border of theirrangeruns almost to the Irtysh, then turns to Zhalaula and descends southward westof the Shiderty River to the Myrzyk ridge (Bayanauyl). To the west, marmotsare found nearKurgaldzhin and Tengiz lakes, in the foothills of Ulutau and in the south of Akmola region, especially along the Terisakkan River. The southern border runsthrough the upper reaches of the Ulkayak and the northern spurs of the MugodjarMountains, further north of the Ilek River. Marmots are notfound in the forests of Kokshetau and in the desolate steppes..
Status.
Habitat. .